| The Diamond Manufacturing Process |
 |
For hundreds of years the Diamond has fascinated man for its alluring sparkle and physical hardness exceeding all other gems. Formed about 3 billion years ago beneth the the Earth’s crust by extreme heat, it may be the oldest item you will ever own. Before the rough diamond is transformed into a beautiful piece of jewelry, it must undergo several stages in its production. |
|
Stage 1 - Mining the Diamond Rough
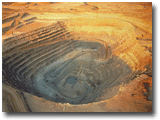
Roughly 50% of diamonds come from Africa, although some sources of diamonds have been discovered in India, Russia, Canada and Australia. The diamonds that made it to the surface were forced up volcanic activity, through kimberlite pipes. A typical pipe mine consists of a large vertical shaft and tunnels running from the main pipe. The deepest mine runs about 160 kilometers, down into the earth with hundreds of tons of rock, gravel and sand that need to be blasted, drilled, crushed and processed to yield just 27,000 kg mined annually. Only about 20% of all rough diamonds are suitable for polishing and the rest are used for industrial purposes. Once the rough is found, it is sold to the manufacturers. |
 |
|
 |
Stage 2 - Rough Reaches the Market
A large proportion of the world’s rough supply goes to De Beers’ Central Selling Organization (CSO). The rough that the Central Selling Organization buys is sorted into more than 5,000 different categories. Once the rough is priced and sorted, it is then sold to manufacturers at sights and there are ten sights yearly, each lasting a week. The chosen few allowed the chance to purchase at these sights are called Sightholders. The balance of the world’s rough supply is sold to private buyers and through private auctions. |
|
Stage 3 - Diamond Manufacturing
Regardless of the source, all rough diamonds eventually end up at the cutting centers. Today, the major cutting centers are Israel, Antwerp, Bombay, Johannesburg, & New York. Upon reaching its destination the rough is carefully examined, now adays with the help of computers, decisions are made on how it should be cut to yield the greatest value. After the stone’s size and shape are determined, taking into consideration the rough’s shape, as well as the quantity and position of its internal inclusions, the stone is marked and usually sawed. The stone then goes through a series of diamond cutters who each have their own specialty. Finally, the diamond is polished and cleaned, all ready for sale. |
 |
|
 |
Stage 4 - The Final Journey
After the diamond is manufactured it needs to be sold but for decades, diamond manufacturers have sold their cut diamonds to jewelry manufacturers and wholesalers who in turn, sell to jewelry diamond dealers and to retail jewelry stores. Today’s Internet technology is changing the diamond market, diamond manufacturers now have a direct link to the final customer. Through the internet, it is possible to purchase the same quality diamond for a significantly lower price because it does away with the middleman. |
|
|


